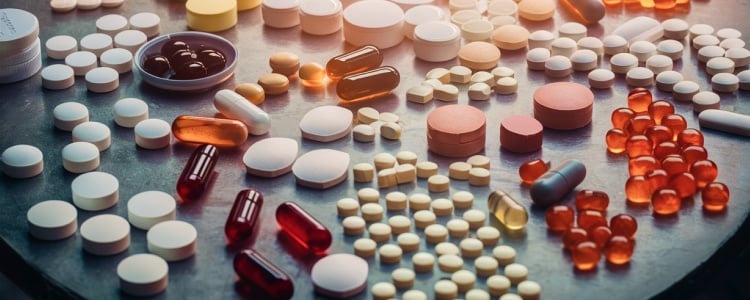
Many years ago the only oral dosage forms available were liquids, powders, tablets and capsules. Today there are a wide range of medication delivery systems to choose from, including various types of pills. Choosing an oral dosage form is a significant product development decision, as medication delivery systems can impact your pharmaceutical or nutraceutical product’s absorption, efficacy, cost, branding and more.
This oral dosage forms comparison explores the difference between tablets and caplets, the role of gummies, and even consumer questions like pill vs tablet vs capsule or softgels vs capsules absorption.
How do delayed-release and immediate-release capsules compare?
Before we get into a discussion of the various dosage forms, it is helpful to first understand delayed-release vs. immediate-release medication.
Most oral dosage forms provide immediate release of the medication or nutraceutical. The dosage is swallowed and quickly gets released and absorbed into the blood stream. While this is appropriate for most formulations, it is not appropriate for all.
Some formulations – such as probiotics and enzymes – can lose efficacy if exposed to the harsh, acidic environment of the stomach. This is why delayed-release oral dosage forms, such as AR-CAPS® Acid-Resistant Capsules and K-CAPS® Delayed-Release Capsules, are available. These particular options, for example, safeguard their contents from stomach acids, delivering nearly all of the formulation directly to the small intestine.
Understanding Pills: The Broad Category of Oral Dosage Forms
A pill is a small round mass of medicine or supplement that is meant to be swallowed whole. Because of this, the question about the difference between tablets and pills is essentially one of classification: tablets, caplets, capsules, and softgels are all types of pills.
Tablets: Benefits, Challenges, and Pharmaceutical Applications
Tablets, which are the most common types of pills, are small, smooth, compressed masses of material. Tablets can be round, oblong or disc-shaped.
Benefits of tablets:
• Cost: Tablets are the least expensive to manufacture of all the medication delivery systems discussed in this article.
• Size: Tablets can be made in a wide range of shapes and sizes.
• Volume: Due to the compression used to form tablets, tablets can pack the most material into a given space.
• Dosing flexibility: Tablets can be made with a scored line running down their center, to make it easier for the consumer to use a pill cutter to split the pill in half to reduce the dose.
• Shelf stability: In general, tablets retain their potency for a longer period of time than liquids, powders and most capsules. They are a very shelf-stable option.
• Tamper resistance: Tablets have excellent tamper resistance.
• Branding: The tablet’s size, shape, color, and imprint can be used for product branding purposes.
Potential drawbacks of tablets:
• Formulation options: Tablets are not an appropriate dosage format for heat-sensitive or low-melting-point formulations or for large-dose actives.
• User-friendliness: A major drawback of tablets is that, in an oral dosage forms comparison, tablets are the most difficult form to swallow. In addition, tablets are not as good at masking the taste and smell of formulations as some other oral dosage formats.
• Inclusion of additives: A variety of additives are used as part of the manufacturing process, to help hold the tablet together and enhance the texture or flavor.
• Manufacturing process: After the material is compressed it must go through a heating process in order to bond the molecules together.
Caplets vs. Tablets: A Smoother Alternative for Easier Swallowing
Caplets are a type of tablet that is smaller in size and coated with a film or gelatin coating. This coating creates a smoother finish that makes caplets easier to swallow than tablets.
Benefits of caplets:
The primary benefits of caplets are the same as those of tablets – they’re simply easier to swallow and do a better job of masking tastes than tablets.
Potential drawbacks of caplets:
The potential drawbacks of caplets are primarily the same as those of tablets. The big difference is that, due to the added coating, they are more expensive to manufacture than tablets.
Two-Piece Hard Capsules: Versatile Solutions for Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Formulations
Two-piece hard capsules are types of pills that are composed of two cylindrical shells that fit together to form a hermetically closed unit. Capsules can be used to encapsulate powders, granules, beads, tablets and liquids – or a combination of these items.
Most two-piece hard capsules are made of either gelatin, which is an animal-based product, or HPMC, a plant-based material. The process of manufacturing the capsules themselves is separate from the process of filling the capsules to make the finished product.
Benefits of two-piece hard capsules:
• Size: Capsules are available in a wide variety of sizes.
• Tamper resistance: Capsules can be made tamper-resistant with the addition of banding.
• User-friendliness: Capsules are tasteless and odorless (with the exception of special flavored capsules), and very easy to swallow. CapsCanada’s K-CAPS® vegetarian capsules are non-GMO; free of preservatives, starches and common allergens; Kosher and Halal certified; and Vegan registered by the Vegan Society. This makes them suitable for consumers with a wide range of special dietary needs and preferences.
• Inclusion of additives: Formulations for two-piece hard capsules can be made without the use of binders or other excipients.
• Manufacturing process: Although tablets have a faster manufacturing process, filling capsules is a much less complicated process than manufacturing softgels, tablets or caplets.
• Absorption: Standard capsules disintegrate quickly, rapidly releasing their contents into the blood stream. Acid-resistant and delayed-release capsules are available for when rapid release is not desired.
• Formulation options: Capsules can be used to encapsulate ingredients that cannot be made into tablets, such as large-dose actives and heat-sensitive or low-melting-point drugs.
• Branding: Capsules offer the most branding possibilities of all the types of pills. Customization options include the capsule type (gelatin, HPMC, delayed-release, acid-resistant, titanium dioxide-free, and more); cap and body color, including a choice of standard, custom and PMS colors; inclusion of banding; color of the optional band; size; finish; flavor; printing, including detailed axial or radial printing on the capsule cap and/or body.
Potential drawbacks of two-piece hard capsules:
• Cost: Capsules are more expensive to produce than tablets.
• Volume: Capsules have significant space and volume limitations, as the contents are not tightly compressed as for a tablet.
• Dosing flexibility: Once a capsule has been filled, the dosing cannot be changed.
Softgels vs. Hard Capsules: Key Differences in Manufacturing and Bioavailability
Softgels are types of pills that are very smooth one-piece capsules with a soft gelatin-based shell surrounding a liquid or semi-solid filling. Softgels are produced, filled and sealed in a single process.
Benefits of softgels:
• Size: Softgels meant for use as an oral delivery form are available in a variety of sizes, in oblong, round, oval and tube shapes. In addition, special shapes, such as those resembling animals or fruits, are also possible.
• User-friendliness: Softgels are extremely easy to swallow. However, they do not mask unpleasant tastes and odors as well as two-piece hard capsules do.
• Shelf stability: Because they are air-tight and completely sealed, softgels have a longer shelf life than two-piece hard capsules.
• Tamper resistance: Softgels are tamper resistant.
• Absorption: Softgels have a dissolution time of 20 to 30 minutes.
• Branding: Softgels’ size, shape, color and imprint can be used for product branding purposes.
Potential drawbacks of softgels:
• Cost: Softgel manufacturing, which is very specialized, is considerably more expensive than manufacturing pharmaceutical or nutraceutical products in tablets, caplets or capsules. A component of these higher costs is gelatin wastage, which equals to up to 40% of the web size.
• Volume: Softgels have significant space and volume limitations.
• Dosing flexibility: Once a softgel has been made, the dosing cannot be changed.
• Formulation options: Softgels are used almost exclusively to encapsulate liquids. Because of their high water content, softgels are primarily used to encapsulate oils and materials that are dissolved or suspended in carrier oils. They are not appropriate for fills that have a high hygroscopicity or a melting point at or above 35° C.
• Inclusion of additives: Softgels, which contain 20 to 30% plasticizers, require the addition of glycerin.
• Manufacturing process: Softgel manufacturing, which requires considerable expertise, is a fairly lengthy process, typically taking three to four days from gelatin prep to blister packing. In addition, softgels have stringent manufacturing conditions, as the relative humidity at room temperature must be kept to between 20 and 30%.
Chewable Tablets: Enhancing Patient Compliance Through Alternative Dosage Forms
Chewables are a type of tablet that is designed for those who cannot or will not swallow a pill, such as children.
Benefits of chewable medications and supplements:
• Size: Chewables can be made in a large variety of sizes and shapes.
• Dosing flexibility: Chewables can be made with a scored line running down their center, to make it easier for the consumer to use a pill cutter to split the medication in half to reduce the dose.
• User-friendliness: Chewables can be a very user-friendly option, especially for children and others who cannot swallow pills.
• Tamper resistance: Chewables have excellent tamper resistance.
• Absorption: Because they are chewed, chewables provide very rapid absorption.
• Branding: The chewable’s size, shape, color, flavor and imprint can be used for product branding purposes.
Potential drawbacks of chewables:
• Cost: Chewables are more expensive on a dollars-per-milligram basis than other dosage formats.
• Volume: Because the formulation must be mixed with flavorings and sugars to make them more palatable, chewables tend to hold less active ingredients than similar-sized tablets.
• Formulation options: Because they are a form of tablet, chewables are not an appropriate dosage format for heat-sensitive or low-melting-point formulations, or for large-dose actives.
• Inclusion of additives: Chewables generally require the addition of flavorings and sugars to make them palatable.
• Manufacturing process: As part of the manufacturing process the material must go through a heating process in order to bond the molecules together. This is why chewables cannot contain heat-sensitive ingredients.
Gummies in Nutraceuticals: Palatable Solutions and Formulation Challenges
Gummies are a chewable oral dosage format that have an appealing taste and a gummy texture.
Gummies, which often look and taste like gummy candies, are used primarily for nutraceutical products.
Benefits of gummies:
• Size: Gummies can be made in a wide variety of standard and custom shapes and sizes.
• Dosing flexibility: Gummies can be made in a range of consistencies, some of which can be easily cut into smaller doses.
• User-friendliness: Because they taste so good, research shows that gummies are not just popular with children. For example, 41% of consumers overall prefer to take vitamins in gummy format.
• Manufacturing process: The taste and consistency of gummies can be customized during the manufacturing process.
• Absorption: Because they are chewed, gummies provide very rapid absorption.
• Branding: The gummies’ size, shape, color, flavor and imprint can be used for product branding purposes.
Potential drawbacks of gummies:
• Cost: Gummies can be more expensive to manufacture than other oral dosage forms. The special equipment needed can be more sophisticated than that what’s needed to make tablets or capsules, and the added sugars and flavorings can dd to the cost as well.
• Volume: The need to include a relatively large amount of sweetener and flavorings reduces the amount of active ingredient that can be incorporated into each dose.
• Formulation options: Gummies present a range of formulation challenges. This includes dosage-related issues and the fact that the manufacturing process makes it difficult to incorporate certain nutrients, such as iron.
• Shelf stability: Gummies are more susceptible to heat and moisture than some of the other dosage formats.
• Inclusion of additives: Gummies are essentially fortified candy, with sugar or an artificial sweetener as one of the main ingredients. Many also contain artificial colors, flavors and other additives.
Conclusion
As this oral dosage forms comparison shows, there are many factors to consider when choosing the ideal oral dosage form for your product. If your analysis shows that capsules are the best choice, CapsCanada offers a full range of extremely high-quality capsules, backed by exceptional customer service and an elite technical service team that is the best in the industry. To learn more about the difference that CapsCanada can make for your products and profitability, or to simply request samples, contact us today at contact@capscanada.com.
Lyfe Group: Innovation in Oral Dosage
CapsCanada is part of Lyfe Group, a collective of Lyfe Group companies committed to capsule innovation. Through advanced R&D, our products provide pharmaceutical and nutraceutical brands with high-quality capsule technologies, from gelatin and vegetarian capsules to specialized solutions like acid-resistant and delayed-release capsules.
References
Mintel, “Vitamins, Minerals and Supplements: US, 2022”